Mapping Urban Bare Land Automaticallyfrom Landsat Imagery with a Simple Index
Li, H.; Wang, C.; Zhong, C.*; Su, A.; Xiong, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.Mapping Urban Bare Land Automatically from Landsat Imagery with a Simple Index. Remote Sens. 2017, 9(3), 249.Doi:10.3390/rs9030249
Abstract:
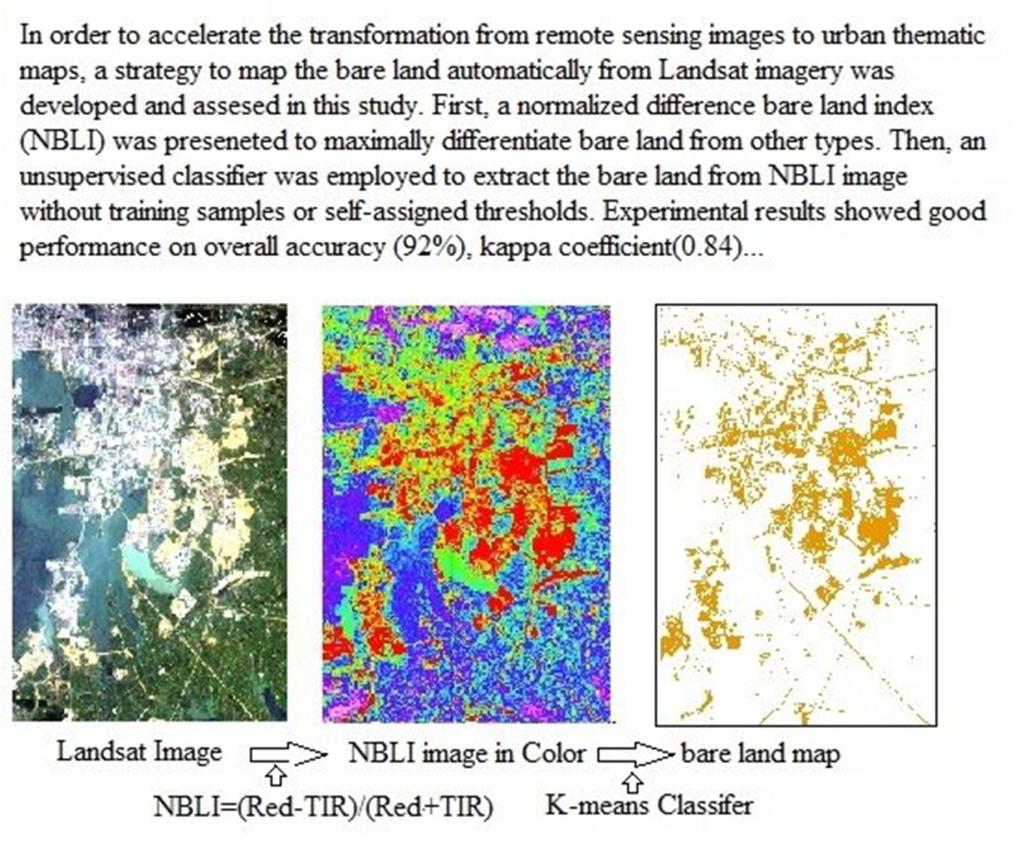
In recent years, hundreds of Earth observation satellites have been launched to collect massive amounts of remote sensing images. However, the considerable cost and time to process the significant amount of data have become the greatest obstacle between data and knowledge. In order to accelerate the transformation from remote sensing images to urban thematic maps, a strategy to map the bare land automatically from Landsat imagery was developed and assessed in this study. First, a normalized difference bare land index (NBLI) was presented to maximally differentiate bare land from other land types in Wuhan City, China. Then, an unsupervised classifier was employed to extract the bare land from the NBLI image without training samples or self-assigned thresholds. Experimental results showed good performance on overall accuracy (92%), kappa coefficient (0.84), area ratio (1.1321), and match rate (83.96%), respectively. Results in multiple years disclosed that bare lands in the study site gradually moved from inner loops to the outer loops since 2007, in two main directions. This study demonstrated that the proposed method was an accurate and reliable option to extract the bare land, which led to a promising approach to mapping urban land use/land cover (LULC) automatically with simple indices.
Keywords: Landsat imagery; the bare land; automatic mapping; spatial-temporal change; LULC.