[SCI论文] Evaluation of landslide mechanisms characterized by high-speed mass ejection and long-run-out based on events following the Wenchuan earthquake
作者:
时间:2015-08-26
点击量:
H.M. Tang, X. Liu*, X.L. Hu, D.V. Griffiths. (2015). Evaluation of landslide mechanisms characterized by high-speed mass ejection and long-run-out based on events following the Wenchuan earthquake. Engineering Geology, 194: 12-24. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.01.004
Abstract:
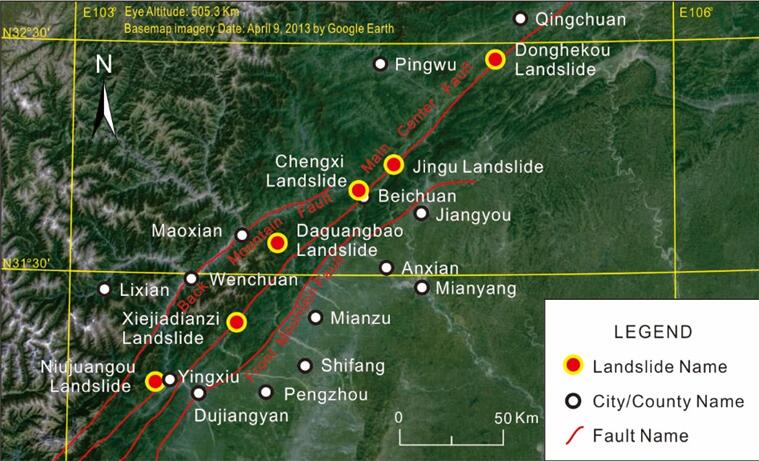
In the 2008Wenchuan earthquake, the mass ejection type of high-speed and long-run-out landslide was an unusual hazard characterized by its dramatic phenomenon of a huge slope mass launching into the air and becoming airborne for a long distance. Quantitative and qualitative combined techniques were applied to reveal the formation mechanism of this type of landslide. Four prerequisites critical to form mass ejection are identified: high position of the toe of the surface of rupture, critical height and critical inclination of slope, sufficient open space in the movement direction, and adequate take-off speed of ski-jump-like mass ejection. These four areaspecific prerequisites provide a promising approach for screening and targeting the potential landslides. Subsequently, a dynamic reliability analysis method that considers the feature of energy–time distribution is proposed. This site-specific method provides a more credible evaluation by emphasizing the most significant period within thewhole earthquake duration. Finally, an aerodynamic inversemethod combinedwith an energy-conservationbased method is applied in the quantitative evaluation to calculate take-off speed of mass ejection. This paper provides a viable solution for regional screening and site assessment for new potential targets of this type of landslide.
Keywords:
Landslide; High-speed and long-run-out; Seismic hazard; Formation mechanism; Reliability analysis; Wenchuan earthquake
 |

